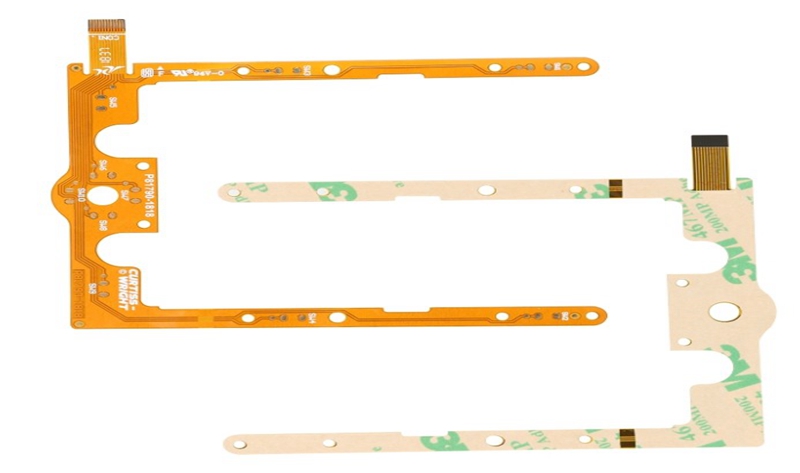
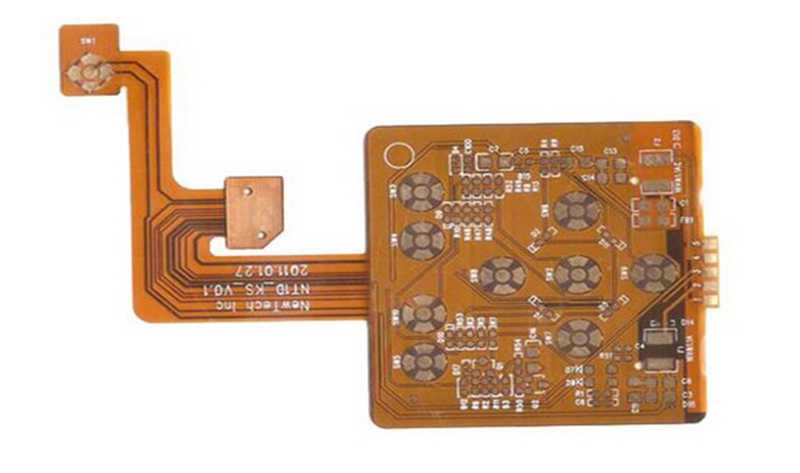
Flexible PCB, its Chinese meaning is flexible printed circuit board, referred to as flexible board. It is made of conductive circuit patterns by using optical imaging pattern transfer and etching process methods on a flexible substrate surface. The inner and outer layers of the double-sided and multi-layer circuit boards are electrically connected through metallized holes. The surface of the circuit pattern is protected and insulated by PI and adhesive layer. It is mainly divided into single panel, hollow board, double panel, Multilayer Flexible PCB, and rigid-flex board.
Multilayer Flexible PCB
There are 6 types of flexible PCB boards:
A. Single panel: There is a line on only one side.
B. Double panel: There are lines on both sides.
C. Hollow plate: also known as window plate (finger window).
D. Layered board: two sides of the line (separate).
E. Multi-layer boards: more than two layers of lines.
F. Flexible and rigid board: A product combining flexible and rigid boards.
The flexible board industry first emerged in Japan, dating back to about 2002. The flexible board industry outside Japan started to sprout in 2003, expanded rapidly in 2005, and declined in 2006. The flexible board industry bottomed out in 2007, and began to recover in 2008.
In 2005, the soft board industry had low thresholds and high profits, attracting a large number of enterprises to enter. In 2006, competition became increasingly fierce, and the phenomenon of oversupply was very serious. Many enterprises had to drop prices again and again to survive, or even lose money. At the same time, downstream customers of the flexible board industry, such as large EMS manufacturers, have added a flexible board department and no longer outsourced the flexible board business, which has made the flexible board industry worse.
Since the beginning of 2008, the global economy has seen a downward trend. Rising oil prices, the subprime mortgage crisis, and food prices have skyrocketed. The global economy has entered a downward path, especially in emerging countries. The decline in demand for FPCs comes from consumer electronics. When the economy is in a downward path, the first to be hit is the demand for these non-rigid consumer electronics products: including mobile phones, notebook computers, flat-screen TVs, LCD monitors, digital cameras, DV and other products.
The following Flexible Board Manufacturer introduces the characteristics of flexible circuit boards:⒈ Short: short assembly time, all lines are configured, eliminating the need for redundant wiring connections:
⒉ Small: Smaller than PCB (hard board), which can effectively reduce the volume of the product and increase the convenience of carrying;
3.Light: Lighter weight than PCB (hard board), which can reduce the weight of the final product;
4. Thin: The thickness is thinner than PCB (hard board), which can improve the softness and strengthen the assembly of the third space in the limited space.
A flexible printed circuit board is a printed circuit made of a flexible insulating substrate. It has many advantages that a rigid printed circuit board does not have:
1. It can be bent, rolled and folded freely, can be arbitrarily arranged according to the requirements of space layout, and can be moved and retracted in three dimensions, so as to achieve the integration of component assembly and wire connection;
2. The use of flexible PCB boards can greatly reduce the volume and weight of electronic products, and is suitable for the development of electronic products in the direction of high density, miniaturization and high reliability. Therefore, flexible PCB boards have been widely used in aerospace, military, mobile communications, laptop computers, computer peripherals, PDAs, digital cameras and other fields or products;
3. Flexible PCB board also has the advantages of good heat dissipation and solderability, easy assembly, and low comprehensive cost. The combination of soft and hard design also makes up for the slight insufficiency of flexible substrates in component carrying capacity.
The above is the information about the flexible PCB board introduced by the PCB Board Factory. Hope to help you.