Today Flexible Board Manufacturer will give you a brief description of several categories of flexible printed circuit boards.
At present, there are four types of flexible circuits: single-sided, double-sided, multilayer, and rigid-flex circuit boards.
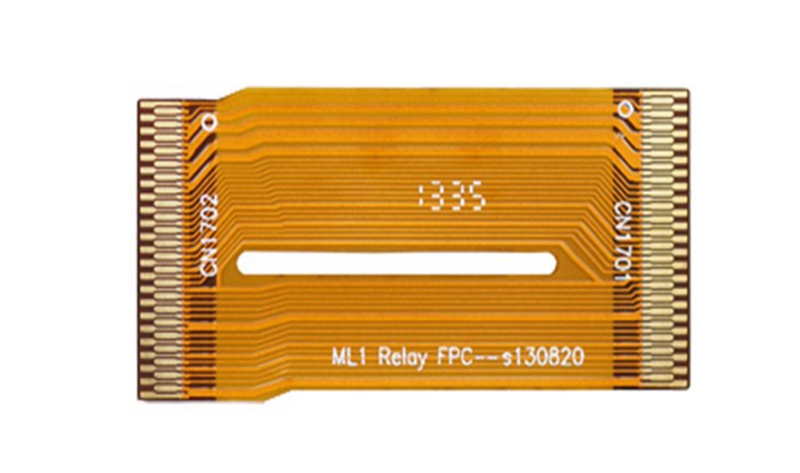
① The single-sided flexible board is the printed board with the lowest cost and low electrical performance requirements. For single-sided wiring, single-sided flexible boards should be used. It has a layer of chemically etched conductive pattern, and the conductive pattern layer on the surface of the flexible insulating substrate is a rolled copper foil. The insulating substrate may be polyimide, polyethylene terephthalate, aramid fiber ester, and polyvinyl chloride.
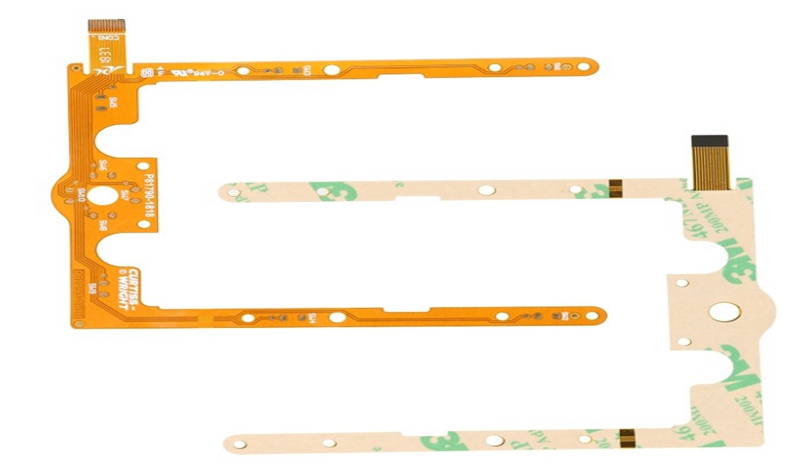
② Double Sided Flexibl PCB is a conductive pattern made by etching one layer on each side of the insulating base film. The metallization holes connect the two sides of the insulating material to form a conductive path to meet the design and use functions of flexibility. The cover film protects single and double-sided wires and indicates where the component is placed.
Double Sided Flexibl PCB
③ Multi-layer flexible board is a single-sided or double-sided flexible circuit with 3 or more layers laminated together, forming metallized holes by drilling collar L, electroplating, and forming conductive paths between different layers. This eliminates the need for complicated welding processes. Multilayer circuits have huge functional differences in terms of higher reliability, better thermal conductivity, and easier assembly performance. When designing the layout, the interaction of assembly size, number of layers and flexibility should be considered.
④ The traditional Rigid Flex PCB is composed of rigid and flexible substrates selectively laminated together. The structure is compact. If a printed board has components on its front and back, a rigid-flex board is a good choice. However, if all the components are on one side, it is more economical to use a double-sided flexible board and laminate a layer of FR4 reinforcement on the back.
The flexible circuit of the hybrid structure is a multilayer board, and the conductive layer is composed of different metals. An 8-layer board uses FR-4 as the inner layer of the medium and polyimide as the outer layer of the medium. The leads extend from the motherboard in three different directions, and each lead is made of different metals. Constantan alloy, copper and gold are used as independent leads. This kind of hybrid structure is mostly used in the relationship between electrical signal conversion and heat conversion, and the electrical performance is relatively harsh, and it is the only feasible solution. It can be evaluated by the convenience of the interconnect design and the total cost to achieve the best performance-price ratio.